When people talk about a company’s success, they often throw around numbers like revenue, sales, or *growth rate. But the truth is, none of those tell the full story. What really shows how healthy a business is? Profit margin. Let’s break down how it’s calculated, why it matters, and what it reveals about a company’s performance.
What Is Profit Margin in Business Terms?
Profit margin is the percentage of revenue that remains as profit after all expenses are deducted. It tells you how efficiently a company turns sales into real profit.
There are a few types of profit margins gross margin, operating margin, and net profit margin and each highlights a different part of your company’s financial performance.
Simply put:
> Profit Margin = (Net Profit ÷ Revenue) × 100
This formula works whether you’re analyzing a small business, an eCommerce brand, or a multinational company.
How to Calculate Profit Margin Step by Step
Let’s keep it simple:
1. Find your total revenue – all the money your business earned.
2. Subtract your total expenses – this includes cost of goods sold (COGS), marketing costs, salaries, and taxes.
3. Divide your net profit by total revenue.
4. Multiply by 100 to get the percentage.
Example:
If your company made £200,000 in sales and had £150,000 in total costs, your net profit is £50,000.
So, Profit Margin = (50,000 ÷ 200,000) × 100 = 25%.
That means you keep 25p of every pound you earn.
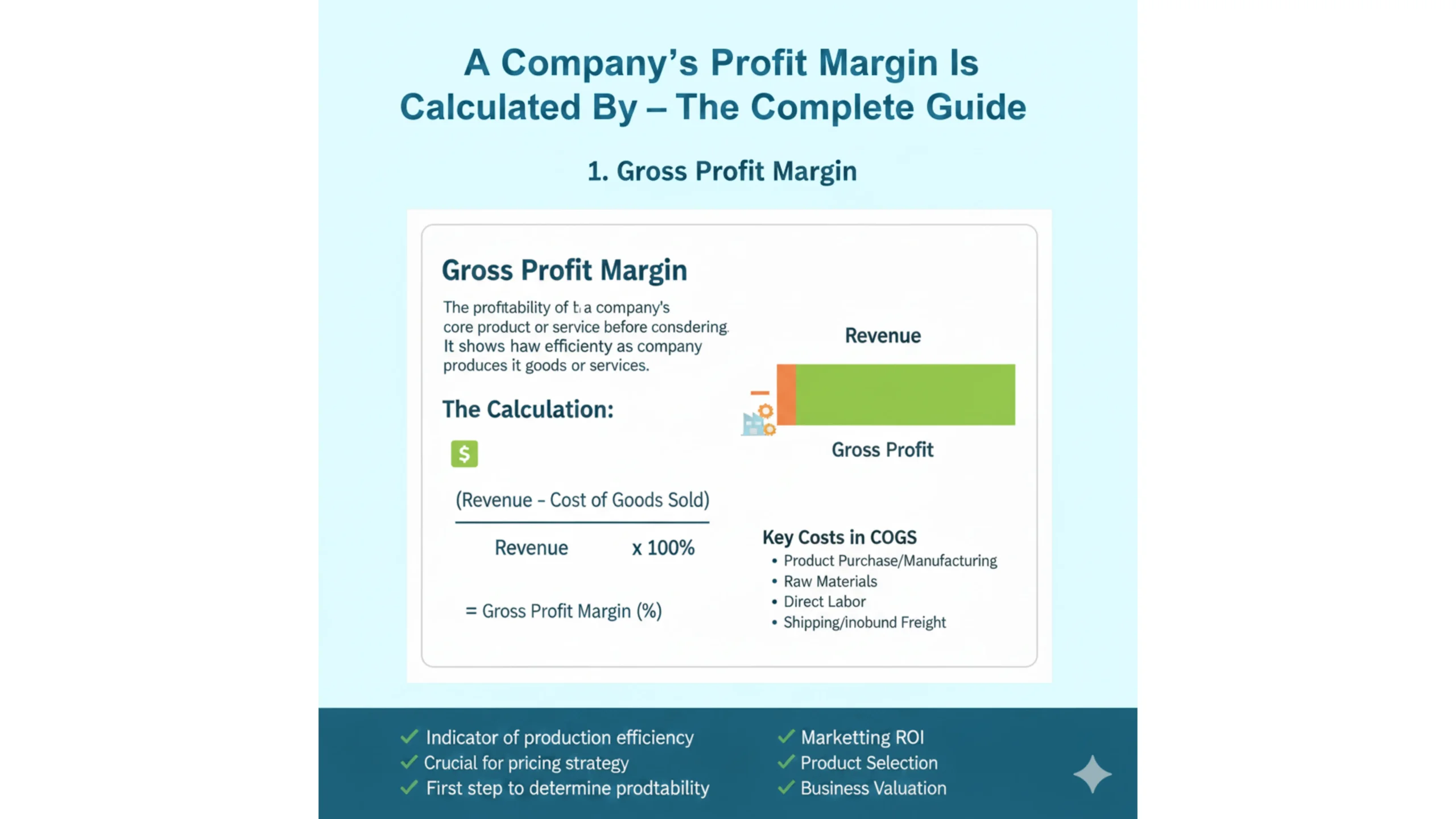
Gross, Operating, and Net Profit Margins Explained
Here’s the thing not all profit margins mean the same thing.
* Gross Profit Margin: Focuses on revenue minus the direct cost of goods sold. It shows production efficiency.
* Operating Profit Margin: Includes operating expenses like rent and payroll — it measures how efficiently you run daily operations.
* Net Profit Margin: The final number after *all* expenses, interest, and taxes. It shows the company’s true profitability.
Understanding all three gives you a full financial picture not just surface-level numbers.
Why Profit Margin Matters for Every Business
Profit margin isn’t just a finance metric; it’s a business health indicator.
It shows:
* Whether your pricing strategy makes sense.
* If your expenses are under control.
* How much room you have for growth or reinvestment.
Investors, lenders, and even potential buyers use profit margins to judge a company’s financial stability and long-term potential.
How to Improve Your Company’s Profit Margin
If your profit margin looks tight, don’t panic it’s fixable. Try this:
* Reduce operating costs without cutting quality.
* Increase prices slightly if your product provides strong value.
* Streamline supply chains and negotiate better deals with vendors.
* Automate repetitive tasks to cut down on labor costs.
* Focus on high-margin products or services that bring in more profit per sale.
The goal is to create a sustainable balance higher efficiency, steady revenue, and consistent profit growth.
Final Thoughts
A company’s profit margin is calculated by comparing net profit to total revenue but what it really reveals is how smartly a business operates. Whether you’re a startup or an established brand, knowing your margin (and how to improve it) gives you control over your financial future.