Introduction to Gross Profit and Gross Margin
Understanding the financial health of a business is crucial, especially in today’s dynamic market. Two terms that often come up are gross profit and gross margin. While they might sound similar, these metrics serve different purposes and provide unique insights into a company’s performance. Whether you’re running an e-commerce store or managing finances for a large corporation, grasping the differences between gross profit vs gross margin can empower you to make informed decisions. Let’s dive deeper into these essential concepts and uncover what sets them apart!
Definition and Calculation of Gross Profit
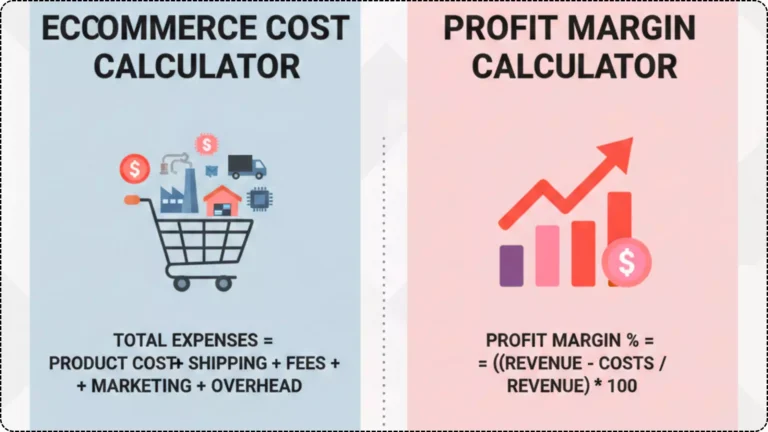
Gross profit is a key financial metric that measures a company’s efficiency in producing goods. It reflects the revenue remaining after deducting the cost of goods sold (COGS). This figure is crucial for analyzing how well a business controls its production costs.
To calculate gross profit, start with total sales revenue. From this amount, subtract direct costs associated with manufacturing or purchasing products. These direct costs typically include raw materials and labor involved in production.
For example, if your business generates $500,000 in sales and incurs $300,000 in COGS, your gross profit would be $200,000.
This calculation provides insight into operational performance and profitability before accounting for indirect expenses like marketing and administration. Understanding gross profit is essential as it lays the groundwork for more detailed financial analysis within any organization.
Definition and Calculation of Gross Margin
Gross margin is a financial metric that represents the percentage of revenue that exceeds the cost of goods sold (COGS). It provides insight into how efficiently a company produces and sells its products.
To calculate gross margin, you subtract COGS from total revenue. This gives you gross profit. Then, divide that figure by total revenue and multiply by 100 to express it as a percentage.
For example, if your business generates $200,000 in sales with COGS amounting to $120,000, your gross profit would be $80,000. Dividing this by $200,000 results in a gross margin of 40%.
Understanding this concept helps businesses assess pricing strategies and production costs effectively while keeping their profitability goals in sight.
Importance of Understanding Gross Profit and Gross Margin
Understanding gross profit and gross margin is crucial for any business owner. These metrics provide insights into the company’s financial health. They help gauge how efficiently a company is producing its products.
Gross profit shows the actual dollar amount left after direct costs, while gross margin offers a percentage that indicates profitability relative to sales. Being aware of both can guide pricing strategies and cost control efforts.
For e-commerce businesses, grasping these concepts leads to informed decisions about inventory management and marketing expenditures. It helps in recognizing which products yield higher returns.
Moreover, investors often scrutinize these figures when considering funding options. A strong understanding can enhance your pitch or lead to better negotiation outcomes with stakeholders. Keeping an eye on both metrics fosters long-term growth and sustainability in today’s competitive market environment.
Key Differences between Gross Profit and Gross Margin
Gross profit and gross margin serve distinct purposes in financial analysis. Gross profit is a raw dollar figure, representing the total revenue minus the cost of goods sold (COGS). It gives a clear picture of how much money a company makes from its core business activities.
On the other hand, gross margin expresses this profitability as a percentage. It shows what portion of revenue remains after covering COGS. This percentage allows for easier comparisons across different companies or industries.
While gross profit can indicate overall sales performance, gross margin offers insight into efficiency and pricing strategy. A high gross profit with a low gross margin may signal that costs are eating away at potential profits. Conversely, both metrics provide valuable insights when evaluating business health but in different contexts.
When to Use Each Metric
Understanding when to use gross profit and gross margin can greatly enhance your decision-making process.
Gross profit is a straightforward figure. It’s ideal for assessing overall profitability from sales. Use it when you need to evaluate how much money remains after covering the cost of goods sold, especially during budgeting or forecasting scenarios.
On the other hand, gross margin provides a percentage perspective. This metric is useful for comparing efficiency across different time periods or among competitors in your industry. Use it to gauge pricing strategies and operational effectiveness.
If you’re analyzing product performance, lean towards gross profit figures. But if you’re exploring market trends or investment opportunities, focus on gross margin percentages instead.
Tailor your approach based on what aspect of financial health you’re investigating. Knowing which metric aligns with your objective allows for informed business choices.
FAQs
How to Calculate Gross Profit from Gross Margin?
-
Gross Profit = Gross Margin (%) × Total Revenue.
What is Walmart’s Gross Profit Margin?
-
Walmart’s gross profit margin is approximately 24–25%.
What’s the Difference Between Gross Profit and Gross Revenue?
Understanding the nuances between gross profit and gross margin is crucial for anyone involved in business finance or accounting. Gross profit represents the raw financial gain from sales after subtracting direct costs, while gross margin provides insight into how efficiently a company produces and sells its products.
Both metrics serve distinct purposes but are interconnected. Gross profit can help evaluate overall profitability, while gross margin offers a percentage-based perspective that aids in comparing performance across different time periods or against industry benchmarks.
When analyzing your eCommerce business’s financial health, keep these definitions and calculations in mind. Knowing when to use each metric will empower you to make informed decisions about pricing strategies, cost management, and growth opportunities. Mastering these concepts can lead to better insights into your company’s operational efficiency and overall profitability in the competitive marketplace of e-commerce.