Many e-commerce businesses focus heavily on revenue, celebrating big sales numbers. However, a high top line doesn’t always translate to a healthy bottom line. Understanding your true profit margin is crucial for sustainable growth and long-term success. This guide will walk you through the essential steps to calculate your e-commerce profit margin accurately, ensuring you know exactly how much money your business is *actually* making.
1. Beyond the Sale Price: Identifying All Costs
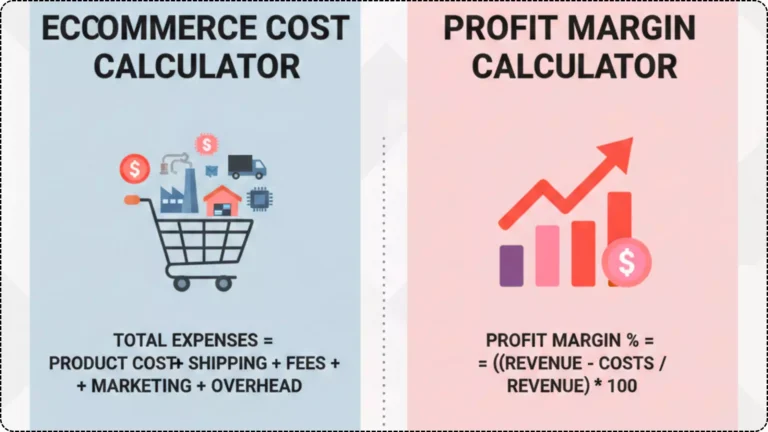
Calculating profit margin isn’t just about subtracting the cost of goods sold (COGS) from your selling price. A truly accurate calculation requires accounting for every expense associated with bringing a product to market and delivering it to the customer.
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): This includes the direct costs of producing your products:
* Raw materials
* Manufacturing labor
* Shipping to your warehouse/fulfillment center
* Packaging materials
Operational Costs: These are the ongoing expenses of running your business:
* Website hosting and maintenance fees
* Payment processing fees
* Marketing and advertising spend (PPC, social media ads, SEO tools)
* Salaries and wages (if not included in COGS)
* Rent for office or warehouse space
* Software subscriptions (CRM, email marketing, accounting)
* Customer service expenses
Shipping & Fulfillment Costs: Often overlooked, these can significantly impact margins:
* Shipping labels and carrier fees
* Packaging and packing labor
* Warehouse storage fees
* Returns processing costs
Accurate tracking of these diverse costs is the bedrock of a reliable profit margin calculation.
2. Gross Profit Margin vs. Net Profit Margin
It’s important to understand the distinction between these two key metrics:
Gross Profit Margin:This figure indicates how much money you make from sales after subtracting only the direct costs associated with producing and selling your products (COGS).
Formula: (Total Revenue – Cost of Goods Sold) / Total Revenue \* 100
Purpose: It shows the profitability of your products before overheads. A healthy gross margin suggests efficient product sourcing and pricing.
Net Profit Margin: This is the ultimate indicator of your business’s profitability. It accounts for all expenses – COGS, operational costs, marketing, shipping, etc. – subtracted from your total revenue.
Formula: (Total Revenue – All Expenses) / Total Revenue \* 100
Purpose: This metric reveals the actual percentage of revenue that turns into profit after all business activities. A strong net profit margin signifies overall business efficiency.
Focusing solely on gross profit can be misleading; net profit margin provides the complete financial picture.
3. Calculating Your True E-commerce Profit Margin
Let’s put it all together with an example.
Imagine your e-commerce store has the following financials for a month:
Total Revenue: $20,000
Cost of Goods Sold (COGS): $8,000
Marketing & Advertising: $2,500
Website & Software Subscriptions: $500
Shipping & Fulfillment (outbound & returns): $1,500
Payment Processing Fees: $300
Other Operational Costs: $700
Step 1: Calculate Gross Profit Margin
Gross Profit = Total Revenue – COGS
Gross Profit = $20,000 – $8,000 = $12,000
Gross Profit Margin = ($12,000 / $20,000) \* 100 = 60%
Step 2: Calculate Total Expenses
Total Expenses = COGS + Marketing + Website/Software + Shipping/Fulfillment + Payment Processing + Other Operational Costs
Total Expenses = $8,000 + $2,500 + $500 + $1,500 + $300 + $700 = $13,500
Step 3: Calculate Net Profit
Net Profit = Total Revenue – Total Expenses
Net Profit = $20,000 – $13,500 = $6,500
Step 4: Calculate Net Profit Margin
Net Profit Margin = (Net Profit / Total Revenue) \* 100
Net Profit Margin = ($6,500 / $20,000) \* 100 = 32.5%
In this scenario, while your gross profit margin is a robust 60%, your true net profit margin, after all expenses, is 32.5%. This significant difference highlights the importance of comprehensive cost accounting.

4. Improving Your Profit Margin
Once you have a clear picture of your current profit margins, you can implement strategies to enhance them.
Optimize COGS:
* Negotiate better deals with suppliers.
* Source materials or products more efficiently.
* Consider bulk purchasing for discounts.
Streamline Operations:
* Automate repetitive tasks to reduce labor costs.
* Improve warehouse efficiency to lower storage and picking costs.
* Regularly review software subscriptions for necessity and cost-effectiveness.
Enhance Pricing Strategies:
* Conduct market research to ensure competitive yet profitable pricing.
* Implement dynamic pricing or tiered pricing for different customer segments.
* Consider offering bundles to increase average order value (AOV).
Reduce Marketing Waste:
* Analyze campaign performance rigorously.
* Focus on channels with the highest ROI.
* Improve conversion rates on your website to make advertising spend more effective.
Manage Shipping & Returns:
* Negotiate better shipping rates with carriers.
* Offer clear shipping policies to reduce customer service inquiries.
* Optimize packaging to minimize shipping weight and damage.
* Analyze return reasons to address product quality or description issues.
Regularly monitoring your profit margins and adjusting your strategies based on data is key to building a financially robust e-commerce business.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I calculate my profit margin?
It’s advisable to calculate your profit margins monthly to identify trends and address issues promptly. Quarterly and annual calculations provide a broader view of your business’s financial health and progress.
What is a good e-commerce profit margin?
A “good” profit margin varies significantly by industry, product type, and business model. Some industries like software or digital products may see margins above 50%, while physical goods often range from 10% to 40%. The most important aspect is that your net profit margin allows for sustainable growth and re-investment in your business.
Can I use accounting software to help with this?
Absolutely. Modern accounting software (e.g., QuickBooks, Xero) and e-commerce analytics platforms can integrate with your sales channels and banks to automate much of the cost tracking and profit margin calculations, providing real-time financial insights.